New topic for 2022/23 - Current page is a rough draft based on old year 7 unit.
1. Safety and the Effects of Acids and Alkalis
Objectives:
- Understand that acids and alkalis can be dangerous and we need to be careful in the lab (and at home).
- Diluting an acid reduces its corrosive effect.
- Heating an acid makes it more dangerous.
|
Many Acids are corrosive - this means that it will damage or destroy other substances with which it comes into contact with by means of a chemical reaction.
Dangerous chemicals, like acid, are made safer by using smaller amounts, or by diluting them by mixing them with water. The acids used in the lab have been diluted with water so that they are often only 1-10% acid. If a chemical is not corrosive, but can still hurt you it is classified as an irritant. It would not cause serious injury, but you would feel a stinging pain if you got a dilute acid on a cut. Many acids are useful in making products that we use daily.
Alkalis are also dangerous. Just like concentrated acids, concentrated alkalis are corrosive. They can attack metals and destroy skin if spilled, so their containers are labelled with a warning symbol. Concentrated alkalis are just as dangerous as concentrated acids, sometimes more dangerous, but many people do not realise this. Strong alkalis are found in cleaners such as oven cleaner. |
2. Tangy Tastes
Objectives:
- Understand that acids are not just found in science labs!
Some acids are safe enough for you to eat or drink, but they are still corrosive.
DO NOT EAT OR DRINK ANYTHING IN THE LAB! (do not even ask if you can eat it!)
Some common foods contain acids.
DO NOT EAT OR DRINK ANYTHING IN THE LAB! (do not even ask if you can eat it!)
Some common foods contain acids.
Acid |
Common Use |
Phosphoric Acid |
Improves flavour in soda |
Citric Acid |
Found in citrus fruits like lemons and oranges |
Ascorbic Acid |
Vitamin C |
Ethanoic (Acetic) Acid |
Vinegar |
Sulphuric Acid |
Car batteries, used to make soap. (Old name: vitriol) |
Hydrochloric Acid |
Found in stomach, used to remove rust (Old name: Muriatic Acid) |
Nitric Acid |
Used to make fertilisers and explosives. |
3. Acids and Bases
Objectives:
- Know that alkalis are the chemical opposites of acids
- Know that alkalis are solutions of chemicals known as bases.
Acids
A chemical term for sour materials that have a pH below 7.0 (on a 14-point scale).
Acids often are capable of eating away at some minerals such as carbonate, or reacting with some metals.
Bases vs alkalis
A base is a substance that can react with acids and neutralise them. Bases are usually:
All alkalis are bases, but only soluble bases are also alkalis
A chemical term for sour materials that have a pH below 7.0 (on a 14-point scale).
Acids often are capable of eating away at some minerals such as carbonate, or reacting with some metals.
- Acids have a sour taste.
- Acids are corrosive.
- Acids change the color of certain vegetable dyes, such as litmus, from blue to red.
- Acids lose their acidity when they are combined with alkalies.
- When acids react with metals, hydrogen gas is released. (As acids always contain hydrogen)
Bases vs alkalis
A base is a substance that can react with acids and neutralise them. Bases are usually:
- metal oxides, such as copper oxide
- metal hydroxides, such as sodium hydroxide, or
- metal carbonates, such as calcium carbonate
All alkalis are bases, but only soluble bases are also alkalis
- Alkalis feel slippery.
- Alkalis change the color of litmus from red to blue.
- Alkalis become less alkaline when they are combined with acids.
4. Indicators
Objectives:
- Know that litmus is a simple indicator of whether something is an acid or an alkali
- Know that there is a Universal Indicator that can also determine the level of acidity/alkalinity of a chemical.
IndicatorsIndicators are substances that will change colour when when they mix with an acid.
Litmus is always red in an acid and blue in a base (alkali)
Litmus is always red in an acid and blue in a base (alkali)
- If litmus stays purple or turns blue then the substance is not an acid.
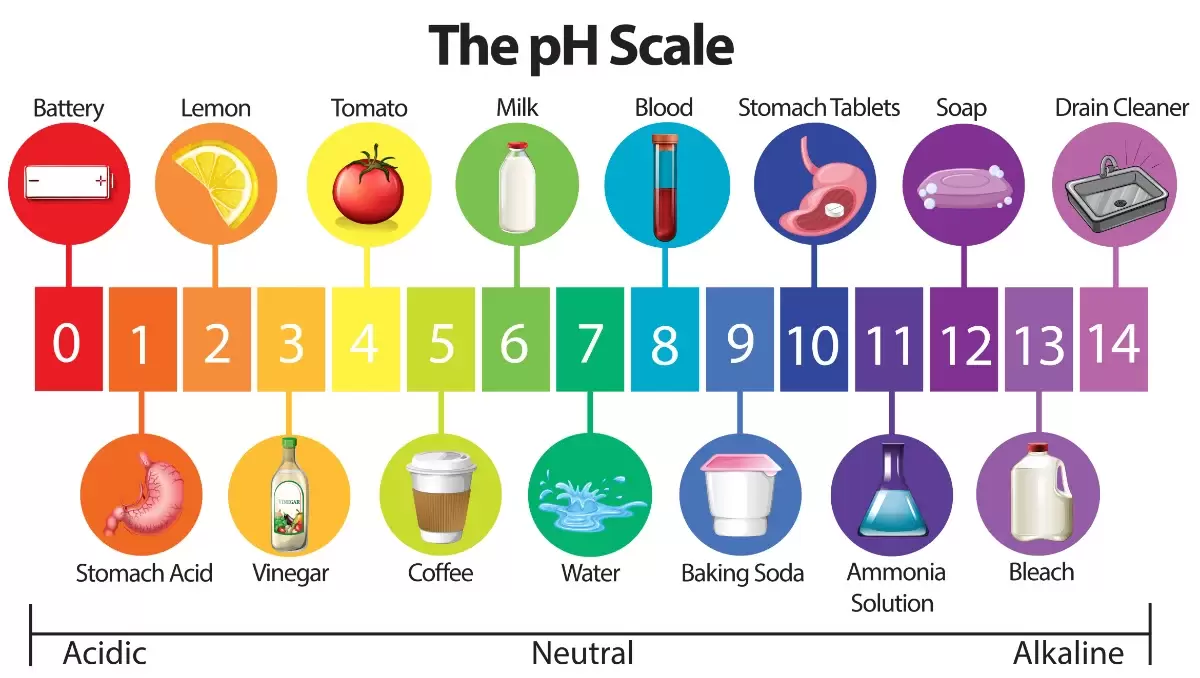
pH is a way to measure how acidic or how alkaline something is.
The pH scale is from 1 to 14.
-pH 1 is the most acidic a substance could be
-pH 7 is neutral and it is found in the middle of the scale
-pH 14 is the most alkaline a substance can be.
Anything with a pH below 7 is acidic. Anything with a pH above 7 is basic.
pH can be tested with substances that change colour when in contact with a solution.
-these types of substances are called indicators.
One of the earliest tests to determine acids from bases was the litmus test.
A chemical patch turned red for acids, blue for bases.
Today chemists can also use pH indicator paper, a pH meter or universal indicator that turns every color of the rainbow to indicate how strong or weak an acid or base is.
The pH scale is from 1 to 14.
-pH 1 is the most acidic a substance could be
-pH 7 is neutral and it is found in the middle of the scale
-pH 14 is the most alkaline a substance can be.
Anything with a pH below 7 is acidic. Anything with a pH above 7 is basic.
pH can be tested with substances that change colour when in contact with a solution.
-these types of substances are called indicators.
One of the earliest tests to determine acids from bases was the litmus test.
A chemical patch turned red for acids, blue for bases.
Today chemists can also use pH indicator paper, a pH meter or universal indicator that turns every color of the rainbow to indicate how strong or weak an acid or base is.
Our skin is naturally slightly acidic; it has a pH of 5.5
Most soaps are alkaline with a pH of about 9 or 10.
Most shampoos or shower gels are slightly acidic, close to the pH of the skin to avoid drying it out!
Checking pH is important for the environment.
Most soaps are alkaline with a pH of about 9 or 10.
Most shampoos or shower gels are slightly acidic, close to the pH of the skin to avoid drying it out!
Checking pH is important for the environment.
- The pH of air and water is checked regularly to make sure that it falls within safe limits.
- This is particularly important near sources of pollution that produce acids.
- Pollution from factories or even exhaust from vehicles can cause acid rain that can harm ecosystems such as wildlife that use freshwater as their habitat.
- Acid rain also corrodes buildings and statues made of limestone.
- Pollution from factories or even exhaust from vehicles can cause acid rain that can harm ecosystems such as wildlife that use freshwater as their habitat.
5. Neutralisation
Objectives:
- Understand that when an acid and an alkali (or a base) react they can neutralise each other.
- Know that one of the products of neutralisation is a SALT.
- To be able to carry out neutralisation experiments with a degree of accuracy.
What happens when an acid is added to an alkali?
The two substances combine, or react, to form a new substance. A chemical reaction has occured.
If exactly the right amounts of acid and alkali are mixed together a neutral solution results.
This is called a neutralization reaction.
The two substances combine, or react, to form a new substance. A chemical reaction has occured.
If exactly the right amounts of acid and alkali are mixed together a neutral solution results.
This is called a neutralization reaction.
Another way of changing the pH of an acid or an alkali is to dilute it by adding water to it.
The more water that is added the pH will get closer to 7.
The more water that is added the pH will get closer to 7.
In our bodies neutralization reactions occur in the digestive system and in the blood.
- The hydrochloric acid in your stomach, has a pH of 1-2, that helps to break down food.
- if your stomach produces too much acid you may suffer from indigestion.
- Medicine called antacids contain alkalis that work to cancel out some of the acid and help to keep the balance right.
A typical neutralisation reaction would be:
hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide --> sodium chloride + water
Another one that can be carried out in the lab uses the base copper oxide to neutralise sulphuric acid:
sulphuric acid + copper oxide --> copper sulphate + water
Note that there is a pattern to the naming of the salts:
When a carbonate base reacts with acid, carbon dioxide gas is released.
hydrochloric acid + calcium carbonate --> calcium chloride + carbon dioxide + water
When bases and alkalis react with acids, you will always get water. Acids always contain hydrogen and bases/alkalis always contain oxygen.
Other patterns that you may have spotted:
hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide --> sodium chloride + water
Another one that can be carried out in the lab uses the base copper oxide to neutralise sulphuric acid:
sulphuric acid + copper oxide --> copper sulphate + water
Note that there is a pattern to the naming of the salts:
- sulphuric acid --> sulphates
- hydrochloric acid --> chlorides
- nitric acid --> nitrates
- phosphoric acid --> phosphates
When a carbonate base reacts with acid, carbon dioxide gas is released.
hydrochloric acid + calcium carbonate --> calcium chloride + carbon dioxide + water
When bases and alkalis react with acids, you will always get water. Acids always contain hydrogen and bases/alkalis always contain oxygen.
Other patterns that you may have spotted:
- Acids contain non-metallic elements
- Alkalis contain metallic elements.