4.4 - The Conservation of Energy
Objectives:
- To understand the Principle of the Conservation of Energy
- To be apply to apply the conversation of energy to solve complex problems.
The principle of conservation of energy is simple: energy cannot be created or destroyed, but only transferred from one form to another. Generally its application as a tool for problem-solving at AP level is pretty straightforward. We either assume that energy transfers are 100% efficient or have to calculate the energy lost.
e.g. speed of an apple falling:
\[GPE\rightarrow KE\]
\[mg\Delta h=\frac{1}{2}mv^{2}\]
\[v=\sqrt{2g\Delta h}\]
e.g. speed of an apple falling:
\[GPE\rightarrow KE\]
\[mg\Delta h=\frac{1}{2}mv^{2}\]
\[v=\sqrt{2g\Delta h}\]
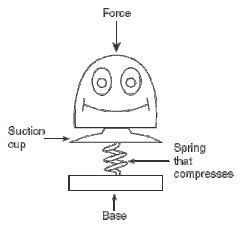
e.g height gained by a spring loaded pop-up toy
|
When the spring is compressed, elastic potential energy is stored within. Once the suction cup releases, this energy is transferred into the kinetic energy of motion, which is in turn converted into gravitational potential energy. Or in shorthand:
\[EPE\rightarrow KE\rightarrow GPE\] \[\frac{1}{2}kx^{2}=\frac{1}{2}mv^{2}=mg\Delta h\] Of course, this assumes that there are no energy losses to heat due to air resistance etc. |
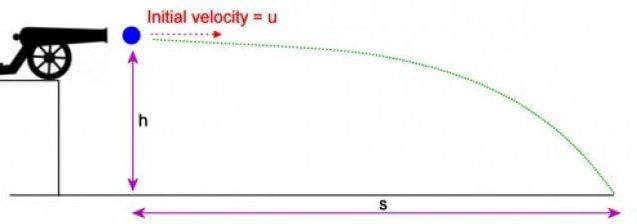
e.g. the launching of a cannonball off a cliff.
|
When the cannonball leaves the cliff top it has BOTH GPE and KE, which get converted to just KE at the bottom. Note that we must ignore energy losses due to air resistance and friction. We can derive the same answer using kinematics and combining the final vertical and horizontal components of the velocities using Pythagoras, but this is far easier!
|
\[GPE + KE_{initial}\rightarrow KE_{final}\]
\[mg\Delta h+\frac{1}{2}mv_{o}^{2}=\frac{1}{2}mv^{2}\]
\[v^{2}=v_{o}^{2}+2g\Delta h\]
TOP TIP #52: Any problem that involves an object moving up or falling can usually be solved by applying the conservation of energy.
However, once we get beyond this practicality and look deeper, we have some difficult questions to ask/answer. Where did the energy originally come from? What will happen once it has all been transferred to heat? These are mind-blowing concepts!
\[mg\Delta h+\frac{1}{2}mv_{o}^{2}=\frac{1}{2}mv^{2}\]
\[v^{2}=v_{o}^{2}+2g\Delta h\]
TOP TIP #52: Any problem that involves an object moving up or falling can usually be solved by applying the conservation of energy.
However, once we get beyond this practicality and look deeper, we have some difficult questions to ask/answer. Where did the energy originally come from? What will happen once it has all been transferred to heat? These are mind-blowing concepts!
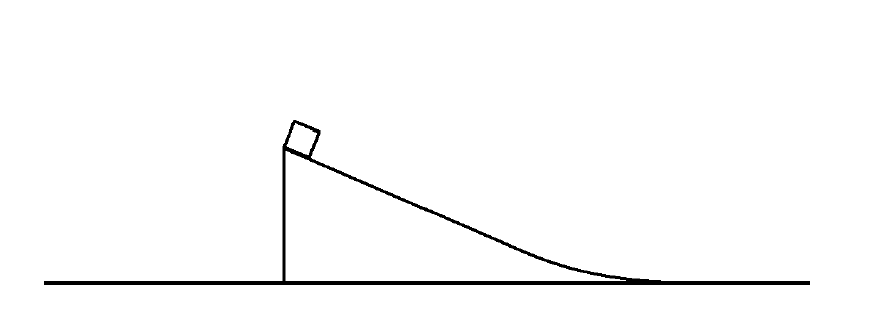
Example of an AP-1 Question on the Conservation of Energy.
|
A block is positioned at the top of a frictionless wedge-shaped ramp. Two experiments are performed.
|
There is a lot of physics in this question. The answer is Experiment A, but why?!