Home >> Oceanography
This is a senior-year internal course. We will focus mainly on the physical aspects of the oceans and their measurement and how they affect the climate and weather. We will spend some time investigating marine weather forecasting as it deeply affects all who wish to work and study on the oceans. Given our location, the North Atlantic and the waters around Bermuda will get the most attention. The goal is to make this an engaging, practical and interactive course.
Prerequisites: IGCSE maths and a science. More importantly, a love of being on the water.
Outline
|
The World Ocean History and Breadth of Ocean Science and Technology. Origin of the oceans, HMS Challenger, the main oceanographic institutes, industries and careers in ocean and marine science. |
Seawater - why is the sea salty? How to measure the salinity. Effect of changing temperature and salinity on the density. How to extract freshwater from the sea. |
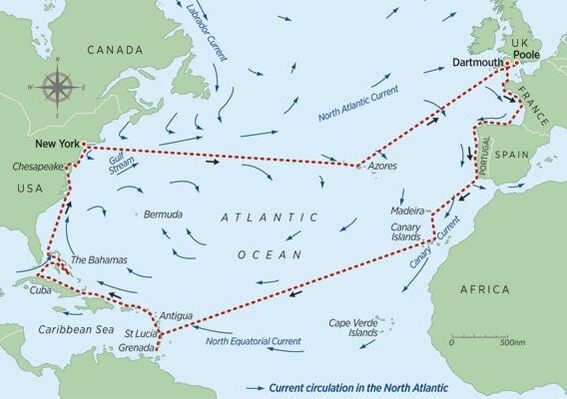
Ocean Circulation and Climate -To include: The Gulf Stream, Thermohaline Circulation and the AMOC, the five gyres. Climate systems, Coriolis effect and El Nino. Atmospheric circulation and Climate |
|
Waves and Tides - To include: how waves are formed, describing and quantifing waves, wave motion above and below the surface, fetch and significant wave height, effect of wind and current on waves, swell and confused seas, tsunamis. |
Observation Systems - Ocean Variables and Measurement. This will be an experimental topic with input from BIOS and involve practical techniques. Also systems such as gliders, moorings, Argo floats, ships, AUVs, satellites, and Remus will be investigated. |
Weather and Navigation - Every mariner who goes to sea is affected by the weather and the ability to know where they are. This section covers the science of weather, forecasting and navigation. |
|
Oceans and Man - Man's effect on the oceans will be studied (maybe as a project?). Ocean acidification, ocean warming, pollution, fish stocks (how can we measure this?), and oceans as a source of food and energy. |
Ocean Literacy Principles (OLP) (links to official website)
These are the ideas that marine scientists and educators agree everyone should understand about the ocean.
These are the ideas that marine scientists and educators agree everyone should understand about the ocean.
- OLP 1: The Earth has one big ocean with many features
The ocean is the defining physical feature on our planet Earth—covering approximately 70 percent of the planet’s surface. Throughout the ocean there is one interconnected circulation system. - OLP 2: The ocean and life in the ocean shape the features of the Earth
Many earth materials and biogeochemical cycles originate in the ocean. The ocean influences the physical structure and landforms of the coast. - OLP 3: The ocean is a major influence on weather and climate
The interaction of oceanic and atmospheric processes controls Earth’s weather and climate by dominating the Earth’s energy, water, and carbon systems. - OLP 4: The ocean makes Earth habitable
Life started in the ocean. Most of the oxygen in the atmosphere originally came from the activities of photosynthetic organisms in the ocean. - OLP 5: The ocean supports a great diversity of life and ecosystems
Ocean life ranges in size from the smallest living things, microbes, to the largest animal on Earth, the blue whale. Most of the organisms and biomass in the ocean are microbes. - OLP 6: The ocean and humans are inextricably interconnected
The ocean affects every human life. It supplies freshwater and oxygen, moderates the climate, influences our weather, and affects human health. - OLP 7: The ocean is largely unexplored
The ocean is the largest unexplored place on Earth—less than 5 percent of it has been explored.
Changes and Ideas for Sept 2021
May be including some marine biology in the course.
Field trips (Snorkling, beach, BIOS, Burt's Island)
Shorten the seawater topic slightly
May be including some marine biology in the course.
- Currents and history of the Mediterranean Sea
- Coral reefs
- Formation of Bermuda
- Marine Biology 101
- Fish - anatomy and function
- whales and dolphins
- Phytoplankton and seaweed/grasses
- Invertebrates
Field trips (Snorkling, beach, BIOS, Burt's Island)
Shorten the seawater topic slightly