This unit takes a look at the Energy Resources and Generating Electricity within the context of cost, the environment, renewable and non-renewable fuels. The emphasis is of course on a sustainable lifestyle – we try to include as much as possible to the situation here in Bermuda.
Student booklet - November 2020
Voltage and Circuits
- List the components in a circuit
- Use a model to explain how changing the voltage affects the current in a circuit
Energy Transfer
- Describe ways in which energy is stored and transferd
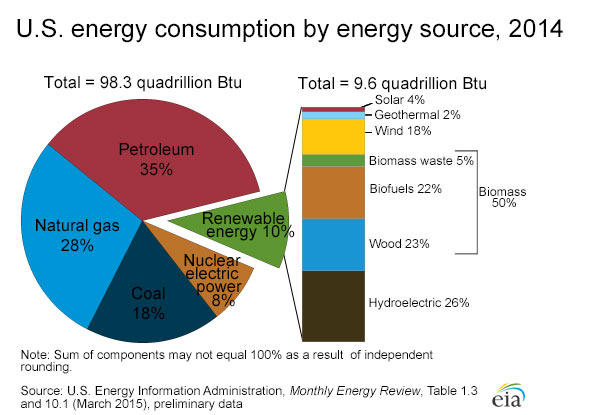
- Know that energy resources are required for everyday life
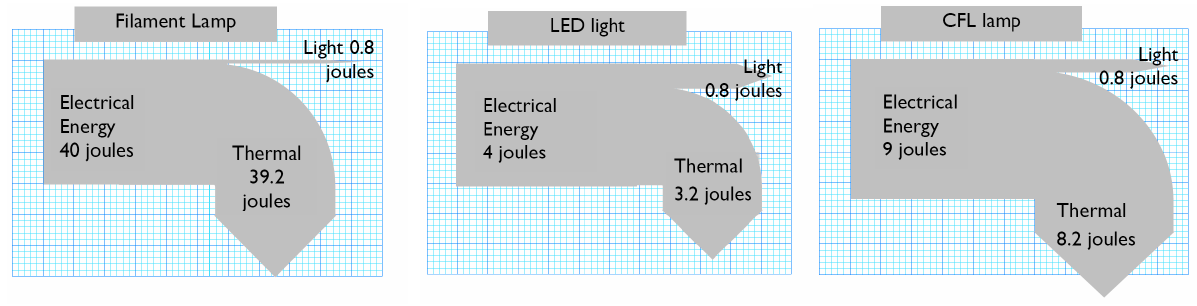
- Draw a Sankey Diagram
- Explain what efficiency means
Generating Electricity
- Describe how electricity is generated.
- Consider the advantages and disadvantages of different ways of generating electricity.
- Explain why efficiency is important
There are four ways to produce electricity:
- Friction - which produces static electricity. Not terribly useful for most applications
- Batteries - which store chemical energy that can be converted to electricity. Portable but heavy and expensive. Battery technology is a massive growth area at the moment with the boom in cell phones, laptops and electric vehicles.
- Solar Cells - another growth area, sunlight is converted into electrical energy. Low power.
- Generators - the major provider. Large machines that convert rotational kinetic energy into electricity.
The vast majority of large scale, high power electricity is produced by rotating a generator. This uses the 'magic' of electromagnetic induction. If a magnet is moved in a coil of wire, electricity is produced (induced). The amount of electricity depends on:
The problem is that nature refuses to allow you to get something for nothing, so it requires EFFORT to generate electricity. The more electricity you want to produce, the harder it is to do so. So, generators need something to spin them. In Bermuda, this mean large diesel engines at BELCO.
- speed of the magnet
- strength of the magnet
- number of coils of wire
The problem is that nature refuses to allow you to get something for nothing, so it requires EFFORT to generate electricity. The more electricity you want to produce, the harder it is to do so. So, generators need something to spin them. In Bermuda, this mean large diesel engines at BELCO.
|
|
This a very cool experiment to try at home. In effect it a miniature version of Volta's first practical working battery, which he named a 'Voltaic Pile'. Took him ages to make large ones, then quickly ran out of 'juice'...
You could also try to make one using a piece of copper, aluminium foil and a lemon. |
|
|
|
|
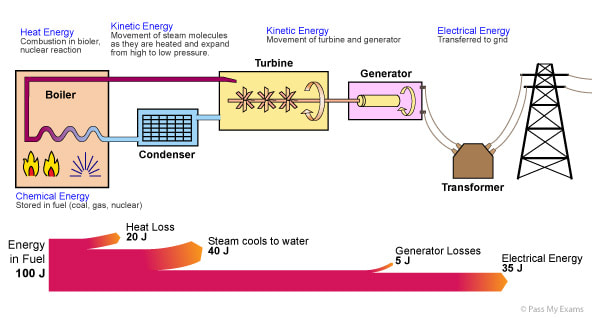
How electricity is generated in big countries (bigger than Bermuda...!). A fuel is burned to boil water. The high pressure steam then turns a turbine (lots of propellers) that in turn spins a generator.
In Bermuda, this is only done at the trash incinerator at Tyne's Bay, which generates about 1.5% of the island's electricity. BELCO skips the water stage and just has 23 huge diesel engines that directly spin the generators. |
|
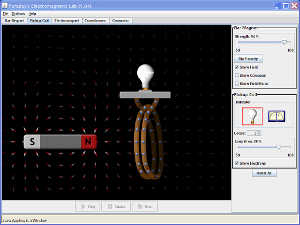
ACTIVITY - run the Java simulation and explore how moving and spinning a magnet produces electricity.
The useful tabs are: 'Pickup Coil' and 'Generator'. |
|
Better Energy Plan for Bermuda - 31 Oct 2018
This was one of the proposals put forward for the future generation of electricity in Bermuda. However, BELCO's plan to continue with newer fossil fuel powered generators won out. Tradition over innovation.... Bermuda Proposals - 31 Oct 2018 Electric Buses - Royal Gazette 15 Nov 2018 |
Fossil Fuels
- Know that energy resources are required for everyday life
- Understand the formation and extraction of fossil fuels
- Know that fossil fuels are non-renewable and polluting, leading to acid rain and global warming
Energy and Power
- Explain what the power rating of an appliance shows
- Explain how we can reduce our energy bills
- Explain how this can help the environment
Using Less Energy (save money!)
- Understand that we can reduce the impact of global warming by using less energy
- Understand that we can save money by using less energy
- Know a variety of methods of reducing energy consumption
Alternative Energy Resources
- Recall a variety of alternative energy resources
- Explain the difference between non-renewable and renewable energy resources
- Explain some of the advantages and disadvantages of various energy resources
Other Resources
|
|
Current Vehicle Rental (Twizy) - Bermuda's NEW rental cars!
|